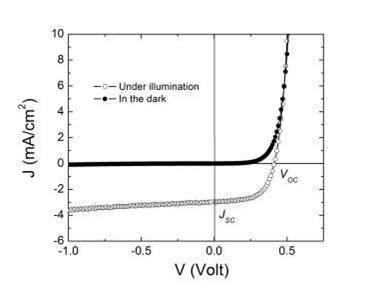
open circuit voltage: where the electron current density is zero.
JSC: The photo current is referred to as the short circuit (SC) photocurrent.
A cathode: obtain electrons.
Anode: lose electrons.
Positive electrode: High voltage.
Negative electrond: low voltage.
,
PCE: PCE= Poutput/P(solar energy)= FF*Voc*Jsc/P(solar energy)


Except for the beyond equations, we also need learn:
Exciton binding energy: = E(affinity)-E(ionization)-E(optical gap) (HOMO and LUMO are not necessarily to be ionization and affinity energy.)
E(optical gap): the threshold for photons to be absorbed.
In almost all inorganic semiconductors, such as silicon, gallium arsenide, etc., there is very little interaction between electrons and holes (very small exciton binding energy), and therefore the optical and electronic bandgap are essentially identical, and the distinction between them is ignored. However, in some systems, including organic solar cells, the distinction may be significant.
generalized Shockley equation:
Onsager model: